Brass Self Tapping Inserts, Brass Inserts
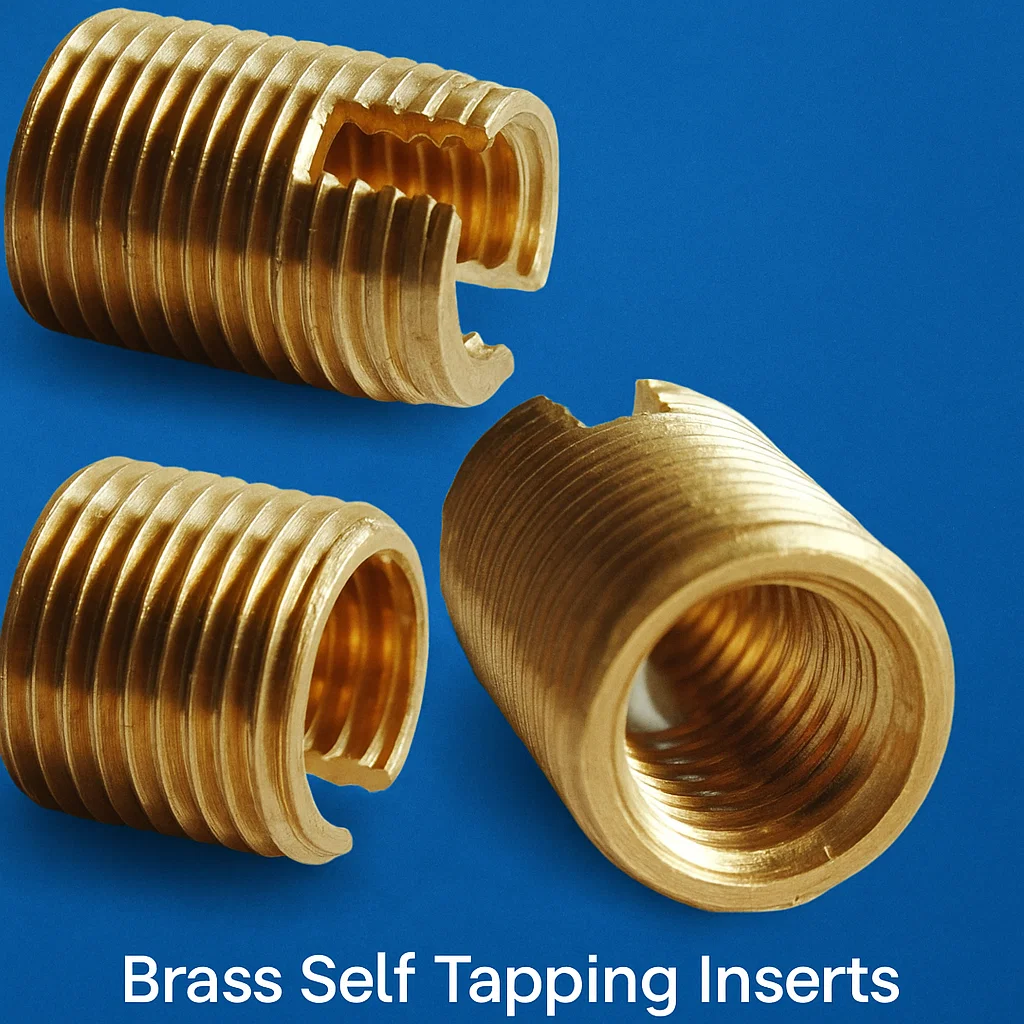


Brass Self Tapping Inserts: High precision Brass Inserts
Price: US$ 9.50/kilogram
What Are Brass Self Tapping Inserts?
Brass self tapping inserts are specialized threaded fasteners that create their own thread path when installed into pre-drilled pilot holes. Unlike traditional threaded inserts that require pre-tapped holes, self-tapping brass inserts feature cutting edges that allow them to tap threads directly into the host material during installation. These inserts consist of an externally threaded body that secures into the host material and an internally threaded core that accepts standard machine screws or bolts.
Superior Material Properties
CZ121 and CW614N brass alloys provide excellent mechanical properties including high tensile strength, superior corrosion resistance, and outstanding electrical conductivity, making these inserts ideal for both structural and electrical applications.
Self-Threading Design
The innovative self-threading mechanism eliminates the need for pre-tapping, featuring precision-cut threads and tapered leads that automatically create perfect thread engagement in the host material.
Vibration Resistance
Advanced thread geometry and brass material properties provide exceptional resistance to vibration loosening and pull-out forces, ensuring long-term reliability in dynamic applications.
Complete Size Specifications Table
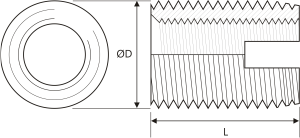
| Internal Thread | Available Lengths (L) mm | External Thread (ØD) | Pilot Hole Diameter (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M3 | 6 | M5 x 0.5 | 4.6 – 4.8 |
| M4 | 8 | M6.5 x 0.75 | 5.8 – 6.2 |
| M5 | 8 / 10 | M8 x 1.0 | 7.1 – 7.6 |
| M6 | 8 / 10 / 12 | M9 x 1.0 | 8.1 – 8.6 |
| M6 | 14 | M10 x 1.5 | 8.6 – 9.4 |
| M8 | 12 / 15 | M12 x 1.5 | 10.6 – 11.4 |
| M10 | 15 / 18 | M14 x 1.5 | 12.6 – 13.4 |
| M12 | 22 | M16 x 1.5 | 14.6 – 15.4 |
Technical Specifications and Material Properties
Brass Alloy Specifications
Installation Process for Brass Self Tapping Inserts
Pilot Hole Preparation
Drill pilot holes to the precise diameter specified in the size table. Hole depth should exceed insert length by 1-2mm. Ensure holes are clean, straight, and deburred for optimal thread engagement.
Insert Alignment
Position the brass self tapping insert perpendicular to the surface. The tapered lead should enter the pilot hole smoothly without forcing or cross-threading.
Threading Installation
Using appropriate installation tooling (hex key, slotted driver, or specialized insert tool), rotate the insert clockwise with steady, even pressure. The self-tapping threads will cut into the material automatically.
Torque Control
Apply controlled torque according to material specifications. Over-tightening can damage threads or crack thin materials. Stop when insert head is flush with or slightly below surface level.
Final Inspection
Verify proper thread engagement, check for cracks in host material, and test with appropriate machine screw to ensure smooth threading and proper fit.
Key Benefits of Brass Threaded Inserts
Performance Advantages
Corrosion Resistance: Brass naturally resists oxidation, moisture, and many chemicals, providing long-term durability in harsh environments.
Electrical Conductivity: Excellent electrical properties make brass inserts ideal for grounding applications and electrical connections.
Vibration Resistance: Superior thread engagement and material properties resist loosening under dynamic loads and vibration.
Temperature Stability: Brass maintains mechanical properties across wide temperature ranges, suitable for both hot and cold applications.
Non-Magnetic Properties: Brass is non-magnetic, making it suitable for sensitive electronic and precision applications.
Machinability: Easy to modify, trim, or machine if custom lengths or features are required.
Industrial Applications
Material Compatibility Guide
Optimal Host Materials
Metals: Aluminum alloys, steel (mild to medium carbon), stainless steel, copper alloys, magnesium alloys
Plastics: ABS, Nylon (PA), Polycarbonate (PC), POM (Delrin), PEEK, Fiberglass-reinforced plastics
Composites: Carbon fiber composites, Fiberglass laminates, Phenolic materials
Other Materials: Dense hardwoods, Engineered wood products, High-density foams
Thread Engagement Considerations
For optimal performance, ensure minimum thread engagement of 1.5 times the bolt diameter in metals and 2-3 times in softer materials like plastics. The self-tapping design creates strong, reliable threads even in materials with lower shear strength.
Installation Tools and Equipment
Required Installation Tools
Drilling Equipment: Variable speed drill, precision drill bits, countersinking tools, deburring tools
Installation Tools: Hex key sets, slotted screwdrivers, specialized insert installation tools, torque-limiting drivers
Measurement Tools: Calipers, depth gauges, thread pitch gauges, hole diameter gauges
Safety Equipment: Safety glasses, work gloves, dust masks, hearing protection
Installation Safety Guidelines
Always wear appropriate PPE during installation. Ensure proper ventilation when drilling certain materials. Use correct pilot hole sizes to prevent material cracking or insert damage. Never exceed recommended installation torque values. Clean holes thoroughly before insert installation to ensure optimal thread engagement.
Quality Control and Standards
Manufacturing Standards
Brass self tapping inserts are manufactured to strict quality standards ensuring dimensional accuracy, thread quality, and material properties.
Testing and Validation
Each batch undergoes comprehensive testing including tensile strength verification, thread pitch accuracy, dimensional inspection, and corrosion resistance testing to ensure consistent performance across all applications.
Maintenance and Service Life
Expected Service Life
When properly installed, brass self tapping inserts provide decades of reliable service. The brass material naturally develops a protective patina that enhances corrosion resistance over time. Regular inspection should focus on thread wear, host material integrity, and torque retention.
Maintenance Recommendations
Periodic inspection of high-stress applications, proper lubrication when specified, protection from galvanic corrosion when used with dissimilar metals, and replacement of inserts showing signs of thread damage or excessive wear.





